What Is a Forged Engine?
A forged engine is built using components shaped under extreme pressure from solid pieces of metal, rather than being poured and set into molds like cast parts. This manufacturing difference might sound subtle, but it has a huge impact on performance, strength, and durability.
So, what exactly sets forged engines apart? Why do enthusiasts, racers, and high-performance builders often choose forged components over cast ones?
In this article, we’ll explore:
- What is Forging?
- How are forged engines made?
- The History Of Forged Engines
- Benefits Of Forged Engine Parts
- Disadvantages of Forged Engine Parts
By the end, you’ll have a clearer understanding of what makes forged engines stand out, and why they’re often considered the stronger and more reliable option for those pushing their vehicles to the limit.
What Is Forging?
Forging is a time-tested manufacturing process used across countless industries, from automotive and aerospace to construction and heavy machinery. Unlike casting, where molten metal is poured into a mold, forging relies on controlled force to reshape solid metal into strong, reliable components.
The process begins by heating a piece of metal until it becomes malleable, but not fully melted. Skilled tools like hammers, presses, or dies are then used to compress and shape the material into the desired form. This not only creates precise designs but also strengthens the internal structure of the metal, making forged parts tougher and more resistant to stress.
There are several types of forging techniques, and the method used often depends on the application:
-
Hot forging: Metal is heated to very high temperatures, making it easier to manipulate and ideal for producing complex shapes.
-
Cold forging: Done at or near room temperature, this method requires more force but results in an exceptionally strong and accurate part.
Thanks to its versatility and strength, forging continues to be a preferred manufacturing method when performance, safety, and durability are critical.
How are forged engines made?
The journey of a forged engine part begins with a solid block of metal, typically steel or aluminum alloy. This metal block is preheated to a high temperature and then subjected to hammering or pressing under extreme pressure. The intense pressure deforms the metal into the desired shape, while the heat ensures that the metal becomes malleable enough to be shaped without cracking.
This process is meticulously controlled to align the metal's grain structure, which results in components that are not only stronger but also more durable. The alignment of the grain structure is a key factor in enhancing the mechanical properties of the forged part, ensuring it can withstand the high stress, temperature, and pressure conditions typically encountered in engine operation.
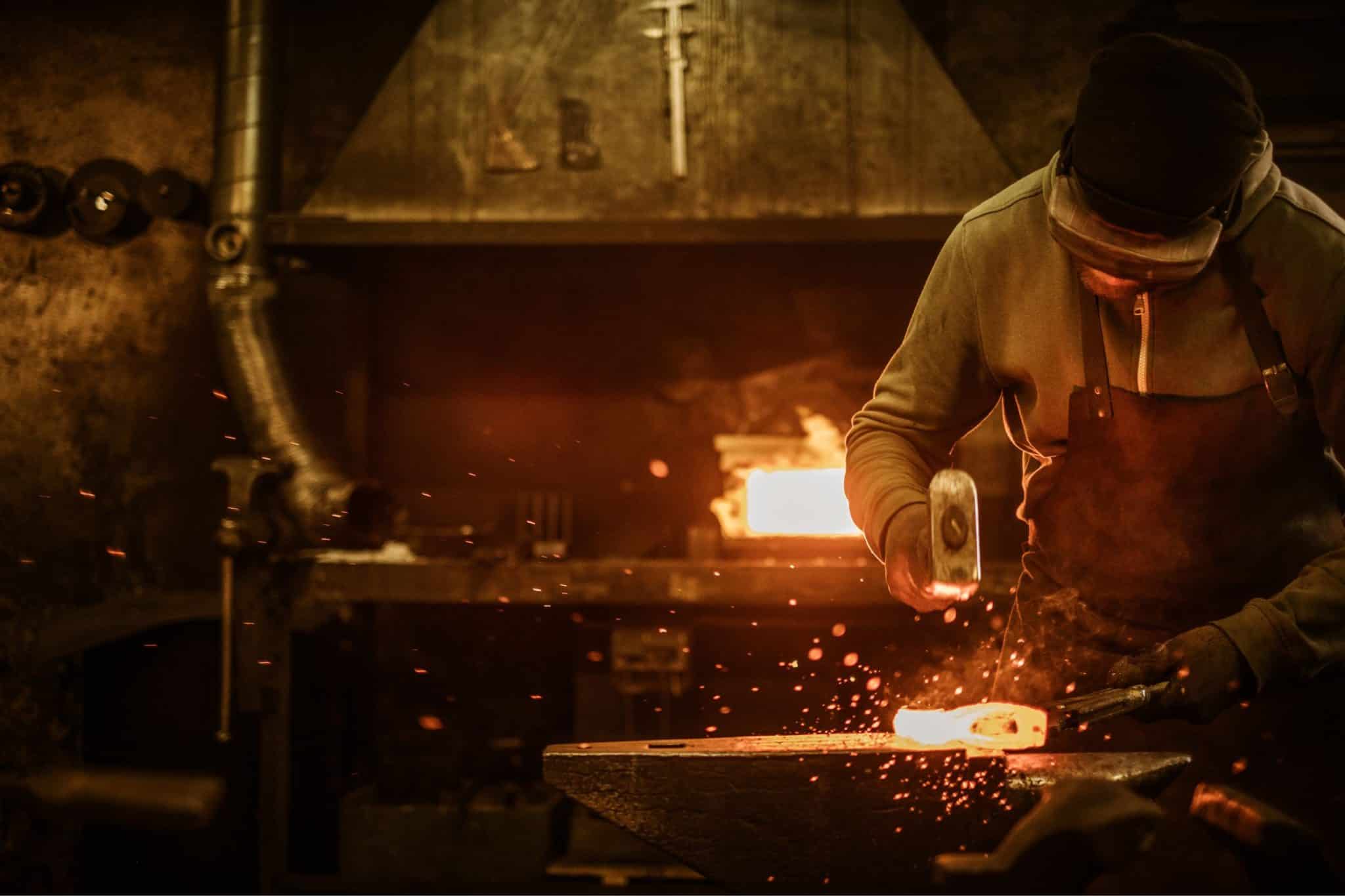
The history of forged engines
The history of forging dates back thousands of years, with its origins traced to ancient civilizations that used primitive forging techniques to create tools and weapons. The industrial revolution marked a significant advancement in forging technology, enabling the production of more complex and robust components.
In the context of engines, the shift to forged parts gained momentum in the early 20th century. As automotive and aerospace industries advanced, the demand for high-performance, reliable engine components grew. Forged crankshafts, connecting rods, and other critical parts became standard in high-stress applications due to their superior strength and fatigue resistance compared to cast parts.
Benefits of Forged engine parts
Key Benefits of Forging
-
Strength and Durability
One of the biggest advantages of forging is the way it transforms the internal structure of the metal. During the process, the grain of the material is compacted and realigned, which significantly improves its mechanical properties. The result? Components that are exceptionally tough, resistant to fatigue, and capable of withstanding extreme stress and harsh operating conditions. This makes forged parts especially valuable in high performance engines, aerospace systems, and heavy duty machinery where failure is simply not an option. -
Weight and Precision
Forging isn’t just about brute strength, it’s also about precision. Because the process allows for tight dimensional control and consistent tolerances, manufacturers can create parts with thinner walls and reduced weight without compromising durability. This lighter yet stronger balance is a huge advantage in automotive and aerospace industries, where every gram saved can improve efficiency and performance. In contrast, casting often introduces small dimensional variations that may require additional machining to achieve the desired specifications.

Disadvantages of Forged engine parts
While forging offers undeniable strength and reliability, it isn’t without its downsides. Like any manufacturing method, it comes with certain limitations that need to be considered:
-
Expense: Forging typically costs more than other processes such as casting or machining. The higher price is due to the specialized equipment, skilled labor, and intensive energy requirements involved. It’s not a quick or budget-friendly option, which is why forged parts are often reserved for applications where performance outweighs cost.
-
Time-Intensive: Forging is rarely a fast process. Metals must be heated to exact temperatures before they can be shaped, and the forming process itself requires precision and control. Compared to methods like casting, which can produce multiple parts at once, forging usually takes longer and demands more oversight.
-
Design Limitations: While forging is excellent for creating strong, durable parts with relatively straightforward shapes, it isn’t ideal for producing extremely intricate or detailed designs. Casting, by comparison, allows for more complex geometries that would be difficult, or even impossible to achieve through forging alone.
In short, forging is best suited for parts where strength, reliability, and performance are critical, but it may not be the most cost effective or practical choice for every application.
Contact B. B. Price for forged parts
Whether you are looking for a detailed forged engine piece or a larger well designed product, B. B. Price have the forging expertise necessary to bring your imagined creations to life.
We have over 150 years of experience in the forging industry. We provide forging services ranging from hand forging, drop forging, upset forging within our forging processes, alongside galvanizing, pressings, and machining.
Whether you are looking for something unique or need a new supplier for your products, get in touch with B.B. Price today. We are always on hand to help answer your queries and ensure that your specifications are met first time, every time.
You can contact us online today or give our team a call.
We look forward to hearing from you soon!
